Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes without
treatment can lead to short as well as long-term health complications, including
hypoglycemia, nerve damage, vision problems and heart disease. Vision problems may include diabetic retinopathy, cataract, diabetic
macular edema (DME) and glaucoma.
Diabetic retinopathy influences blood vessels in
the light-sensitive tissue called the retina that lines the back of the eye. It
is the foremost cause of vision loss among individuals with diabetes and the
driving cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults.
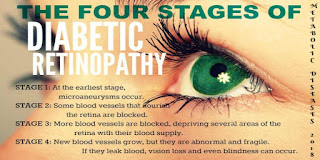
Within the starting
stages, people with diabetic retinopathy may not notice their vision changing.
Diabetics sometimes experience rapid changes in blood sugar that can incidentally
cause blurry vision even when retinopathy is not present. If a person notices a
few specks or spots floating in his visual field, this may cruel he has
developed proliferative diabetic retinopathy, the growth of abnormal new blood
vessels on the retina. High blood sugar levels have been connected in studies
to retinal blood vessel abnormalities. Blurred vision may occur when the
macula--the small area at the center of the retina--swells when it fills with
fluid that has spilled from retinal blood vessels. Since damage to the eye
often develops gradually, early detection of diabetes and control of blood
sugar through diet and medications can make a crucial difference in sparing
vision.
The major risk
factors for developing diabetic retinopathy are high levels of
blood glucose,
pregnancy, hypertension,
high serum lipid and diabetic kidney
disease. Diabetic retinopathy can be detected during a dilated eye exam that
includes: visual acuity
testing, tonometry, pupil dilation, optical
coherence tomography (OCT).
Controlling blood glucose levels can significantly help to prevent diabetes retinopathy and lower the chance of
developing it. Heart disease risk factors also influence retinopathy risk which
includes smoking, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
There are several effective
treatments for diabetic retinopathy which includes a microsurgery called
vitrectomy for repair of eyes with extensive damage and a laser
photocoagulation for moderate stages. Injectable and oral medications that
act on abnormal blood vessels to control diabetic retinopathy are presently in
improvement. Early detection of diabetic retinopathy would be a key to the effectiveness
of these treatments.
For more interesting
information, join International
Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism.



Comments
Post a Comment